Radio approval: Routes to Market Approval for Products with Wireless Technologies

Table of content
The integration of wireless technologies and the consequences for successful radio approval
The choice of wireless technology and its integration into an end device have a significant impact on the certification process. There are three basic options for integrating wireless technologies:
- External wireless modules (e.g. USB dongles): Here, the dongle itself must be certified first and foremost.
- Certified wireless modules: Despite existing certification of the module, the entire product must be tested.
- Uncertified radio chips: This variant also requires full certification of the end product.
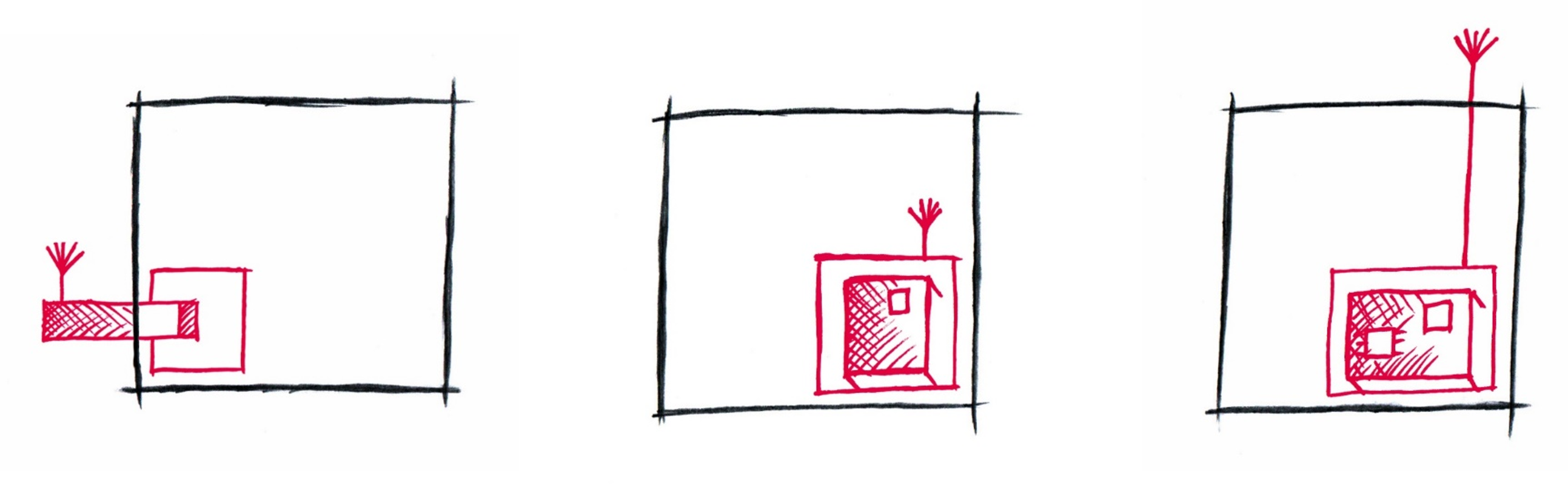
A key finding: Even if a radio module has been certified in advance, this only reduces the testing effort, but does not replace the need for overall product certification. In particular, tests must be carried out on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), radio interference and electrical safety.
Radio approval in Europe & worldwide – Important certification regimes
- CE marking (Europe) The CE marking is mandatory for products within the EU. It confirms conformity with the relevant European standards, in particular the Radio Equipment Directive (RED). Various tests are required for radio approval, depending on the product, intended use and the technologies used:
- EMC tests (e.g. EN 301489-1/-17)
- Radio interference tests (e.g. EN 300 328 for BT/WLAN)
- Electrical safety (e.g. EN 62368-1)
- Health tests (SAR or EMF measurements)
- FCC certification (USA) FCC approval is required for the US market. This is achieved either through full certification via a Telecommunication Certification Body (TCB) or a self-declaration (Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity, SDoC). A special feature since 2023: A “US Agent for Service of Process” must be appointed to fulfill regulatory requirements.
The challenges of global certification
The greatest challenge in international market approval lies in the diverse and sometimes contradictory regulatory requirements. Companies must consider the following aspects:
- Regional differences: No standardized global certification system exists.
- Validity periods: Some certificates are valid indefinitely, others require regular renewal (1-10 years).
- Local requirements: Some countries require additional testing, local representatives or specific product labeling.
For products with built-in wireless technology, countries and regions have different certification requirements:
- RED
- FCC
- National requirements
- Combinations of RED, FCC and national requirements
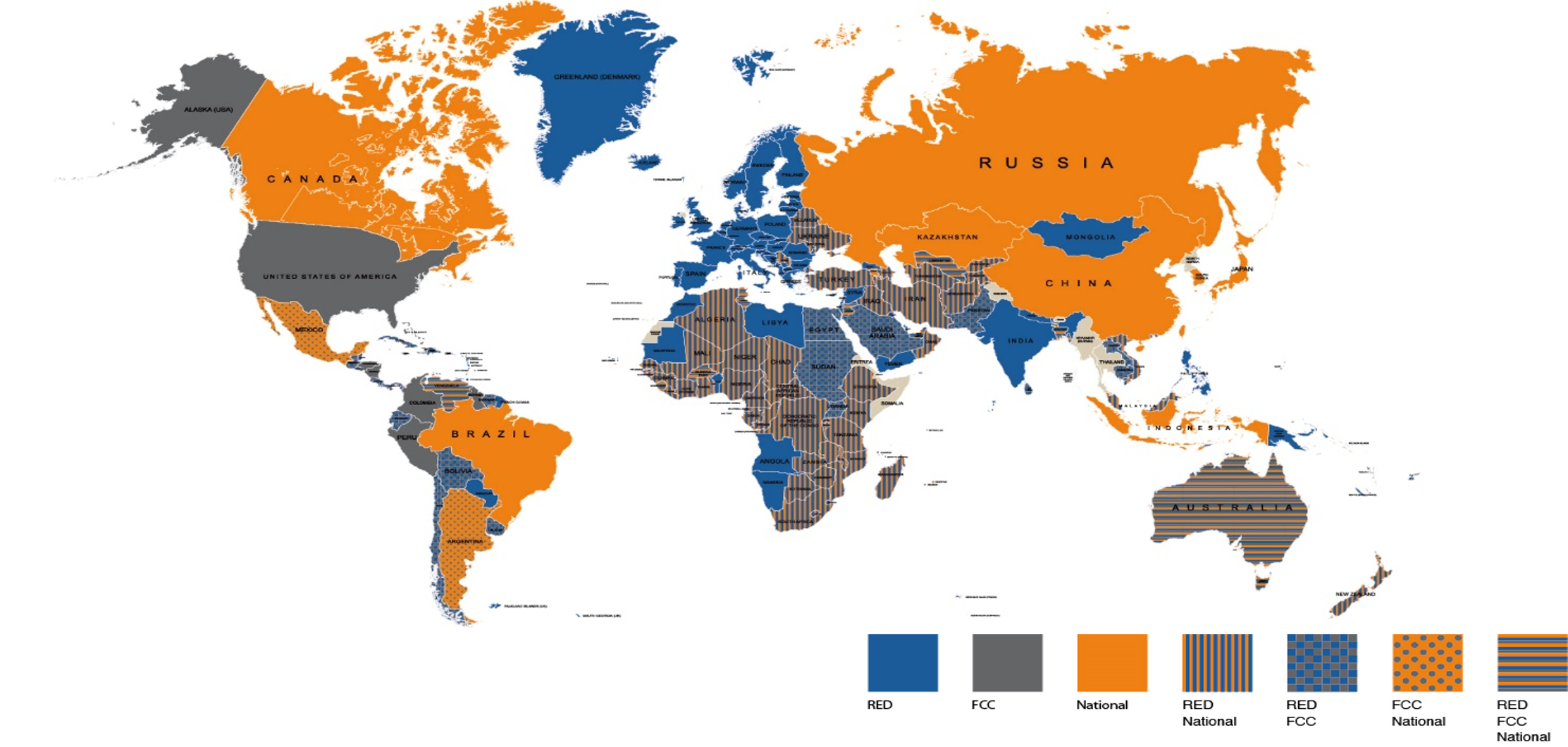
A strategic approach is to obtain CE and FCC approvals first, as many countries recognize these as the basis for their own testing procedures.
Examples:
- ISED (Canada): Separate approval by the Innovation, Science and Economic Development Board is required.
- China: Combination of SRRC, CCC and other test requirements.
- Brazil, Japan, Korea: Own certification processes, partly based on CE or FCC test reports.
Excursus: The importance of private certification regimes
In addition to regulatory requirements, there are voluntary certifications that are regarded as a sign of quality. These certifications are not legally binding for successful wireless approval worldwide, but are perceived by consumers and companies as a seal of quality.
- Wi-Fi Alliance: Tests on the interoperability and performance of Wi-Fi products.
- With this certification, which has no regulatory character but is regarded worldwide as a seal of quality, the devices undergo various tests. Not only the WLAN functionality is tested, but also the interoperability with other Wi-Fi®-certified products.
- Bluetooth SIG: Mandatory certification for products that use Bluetooth and bear the logo.
- In addition to the regulatory approvals for Bluetooth products, approval in accordance with the requirements of the Bluetooth SIG is also required for market launch:
- Every device that wants to use Bluetooth technology and the Bluetooth logo must undergo tests in accordance with the “Bluetooth SIG Qualification Program”.
- Only if these tests are passed is the manufacturer officially authorized to use Bluetooth technology and the associated Bluetooth trademark symbol, which is a global seal of quality for the compatibility of Bluetooth devices.
- Qi certification (Wireless Power Consortium): Prerequisite for the use of the Qi logo for wireless charging.
- In addition to the regulatory approvals for WPT products, approval in accordance with the requirements of the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) is equally required for market launch if the Qi standard is used:
- Any device wishing to use Qi technology and the corresponding logo must successfully pass tests in accordance with the Wireless Power Consortium test specification.
Efficient management with CERT
A key aspect of successful market authorization is the efficient management of certificates and regulatory requirements. Our approval management software CERT offers a comprehensive solution here:
Challenges without digital certification management
- High administrative effort due to manual processes
- Missed deadlines and expired certificates lead to delays and legal risks
- Non-transparent document management makes it difficult to keep track of approvals
- Different country-specific requirements require continuous adaptation
Advantages of CERT for a radio approval
Optimized digital processes and automated workflows can significantly reduce administrative effort. Structured and transparent planning also ensures a faster market launch, as potential delays can be identified and avoided at an early stage.
Fewer manual processes not only lead to lower error rates, but also enable more efficient and precise budget planning. Thanks to a real-time overview, current status updates on certificates and market approvals are available at any time at the touch of a button. This is supplemented by automatic reminder systems that provide early warning of upcoming certificate renewals.

Transparency and compliance with CERT
Central data management enables the clear storage and administration of all relevant certifications. The system supports effective multi-certificate management so that several products and markets can be covered simultaneously. Thanks to its dynamic adaptability, regulatory changes can be implemented quickly and flexibly.
Reports and interactive dashboards provide a transparent visualization of deadlines, status and open tasks. In addition, automated monitoring ensures that expired certificates are detected in good time and audit processes are reliably supported.
Why companies should use CERT
Structured and automated processes significantly reduce time-to-market, enabling faster product launches. At the same time, fewer manual processes lead to lower administrative costs. A centralized solution creates maximum transparency and control across all markets and products. Global compliance with regulatory requirements is also reliably ensured.
The use of specialized approval software such as CERT enables companies to manage the complexity of international certification processes and efficiently launch their products on the market. This means that the entire radio approval process for their own products can be managed quickly and securely worldwide.
Further information on CERT and demo access can be found here: https://cetecomadvanced.com/en/products/cert/
Conclusion
The market approval of products with wireless technologies is a complex process with many regulatory hurdles. However, early planning, the use of existing certifications and structured management of documentation and certificates can simplify the process considerably. Companies that pursue an efficient strategy can bring their products to market faster and more cost-effectively and make the most of international growth opportunities.
In March 2025, we also held a webinar on the basics of market approval in which we went into more detail on the individual topics. You can find the recording of the webinar here: https://cetecomadvanced.com/en/seminars/webinar-on-the-basics-of-market-approval/
Further information:
- EMC tests
- Regulatory radio tests
- Electrical safety tests
- SAR measurements
- CE marking
- FCC certification
- International market approval
- Bluetooth SIG qualification
- Wi-Fi Alliance certification
- Qi certification
- CERT